

The nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear and spindle formation starts. The separation starts from the centromeres and goes towards the end and hence the name terminalisation: The separation of chromosome becomes complete due to terminalisation. Due to this separation the dual nature of a bivalent becomes apparent and hence the name diplotene. They begin to separate from each other except at the chiasmata. The homologous chromosomes condense further. In the region of chiasmata, segments of non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes are exchanged and this process is called crossing over The bivalent thus becomes a tetrad with four chromatids. The two sister chromatids of each homologous chromosome become clearly visible. The chromosomes condense further and become very shorter and thicker. This is called pairing or synapsis. The paired chromosomes are now called bivalents. The adjacent non-sister chromatids are joined together at certain posints called chiasmata. Homologous chromosomes come to-gether and lie side by side throughout their length. Each chromosome consists of two chromatids. The chromosomes uncoil and become large and thinner. It includes 5 sub stages namelyġ.Leptotene 2.Zygotene 3.Pachytene 4.Diplotene 5.Diakinesis This is the longest phase of the meiotic division. The name of each stage is followed by I or II depending on which division of cycle is involved. Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase. During the formation of pollen grains in anther and megaspores in ovules.Įach meiotic division cycle is divided into same four stages as in mitosis. This is how diploids come to possess tow identical sets of chromosomes called homologous chromosomes Meiosis may take place in the life cycle of a plant during any one of the following events.Īt the time of spore formation ie. In these two sets of chromosomes one set is derived from the male parent and the other set from the female parent. During sexual reproduction the two gametes male and female, each having single set oof chromosomes (n) fuse to form a zygote.The zygote thus contains twice as many chromosome as a gamete ( n+n=2n). In all the sexually reproducing organism the chromosome number remains constant generation after generation. The first division is meiotic or reductional in which the number of chromosomes is reduced to half and the second division is mitoticor equational. The two divisions of meiosis are meiosis I or heterotypic division and meiosis II or homotypic division. As a result of this a diploid cell produces four haploid cells.
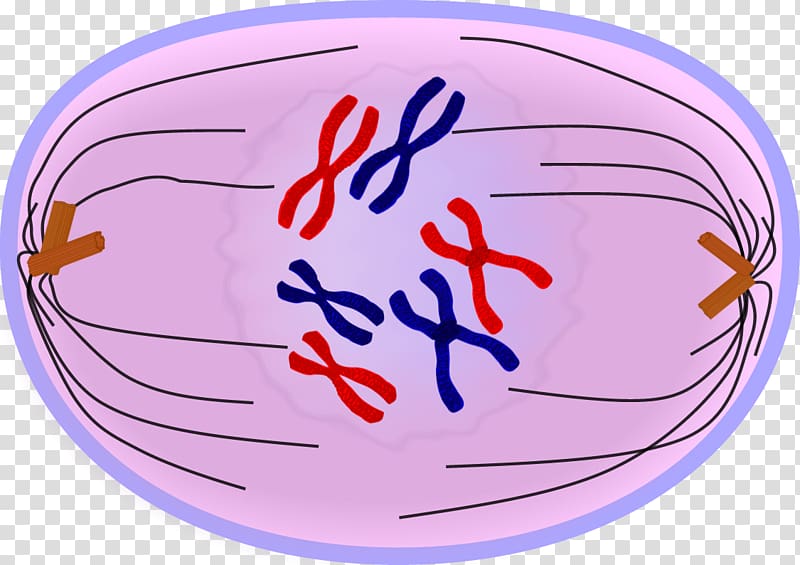
Meiosis consists of two complete divisions. It takes place only in the reproductive cells during the formation of gametes. Meiosis is also known as reduction division(RD) since the number of chromosomes is reduced to half.

Meiosis is a process of cell division of the reproductive cells of both plants and animals in which the diploid number of chromosomes is reduced to haploid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
